Embark on a journey into the fascinating realm of cellular biology with our comprehensive Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet PDF. This meticulously crafted resource provides an immersive learning experience, delving into the fundamental differences between these two distinct cell types.
Prepare to unravel the complexities of cell structure, function, and their profound implications in the ecosystem.
As we delve into the intricacies of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, we will uncover the unique characteristics that set them apart, including their diverse roles in the web of life. Through engaging tables, diagrams, and thought-provoking questions, this worksheet fosters a deeper understanding of these essential building blocks of all living organisms.
1. Introduction to Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
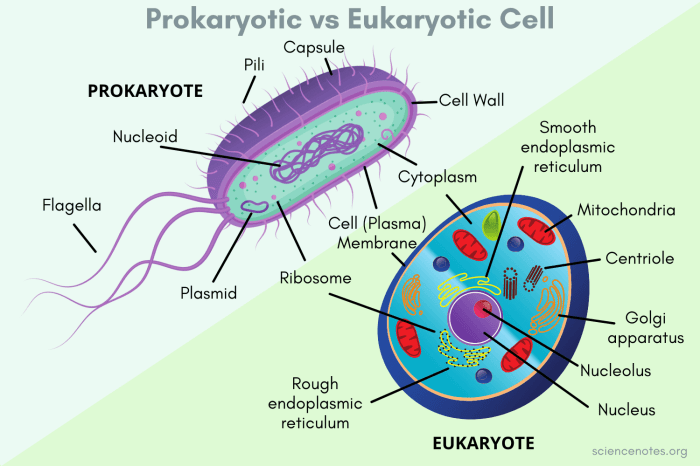
Cells are the basic unit of life and come in two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells and lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles and are more complex and larger than prokaryotic cells.
The table below summarizes the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
| Characteristic | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Absent | Present |
| Size | Smaller (typically 1-10 micrometers) | Larger (typically 10-100 micrometers) |
| Complexity | Simpler | More complex |
2. Prokaryotic Cells: Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet Pdf
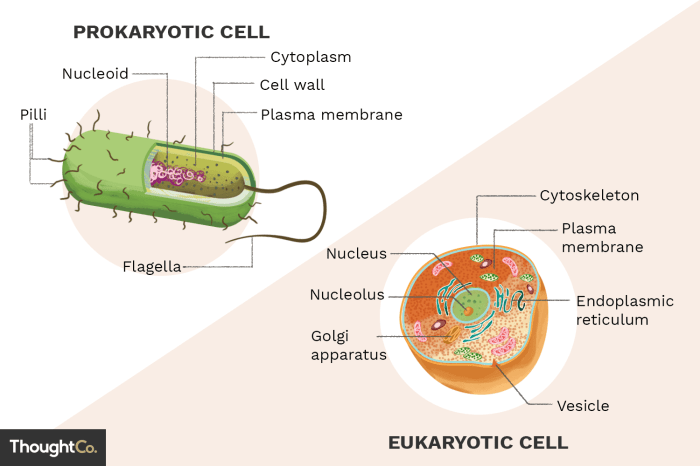
Prokaryotic cells are the simplest and most ancient type of cell. They are found in a wide variety of habitats, including soil, water, and the human body. Prokaryotic cells have a simple structure, consisting of a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA.
They lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
Prokaryotic cells can be divided into two main groups: Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick cell wall that contains peptidoglycan, a polymer of sugars and amino acids. Gram-negative bacteria have a thin cell wall that lacks peptidoglycan.
Prokaryotic cells play an important role in the ecosystem. They are responsible for a wide variety of processes, including nutrient cycling, waste decomposition, and the production of antibiotics.
3. Eukaryotic Cells

Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells and have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are found in a wide variety of organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Eukaryotic cells have a complex structure, consisting of a cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles. The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the cell’s DNA. Other membrane-bound organelles include the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and lysosomes.
Eukaryotic cells play an important role in the ecosystem. They are responsible for a wide variety of processes, including photosynthesis, respiration, and reproduction.
4. Cell Comparison
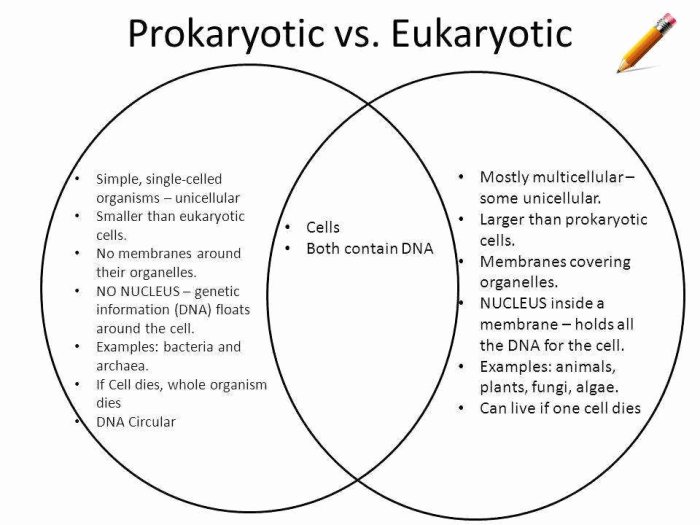
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are two distinct types of cells with different structures and functions. The table below summarizes the key differences between the two cell types:
| Characteristic | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Absent | Present |
| Size | Smaller (typically 1-10 micrometers) | Larger (typically 10-100 micrometers) |
| Complexity | Simpler | More complex |
| Examples | Bacteria, archaea | Plants, animals, fungi, protists |
The differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are thought to have evolved over time. Prokaryotic cells are thought to have evolved from simpler organisms that lacked a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are thought to have evolved from prokaryotic cells that acquired a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles through a process called endosymbiosis.
Top FAQs
What is the primary distinction between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess these structures, resulting in a more complex cellular organization.
How do Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria differ?
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell walls, while Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides.
What is the ecological significance of prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells play crucial roles in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and the production of oxygen and other gases essential for life on Earth.