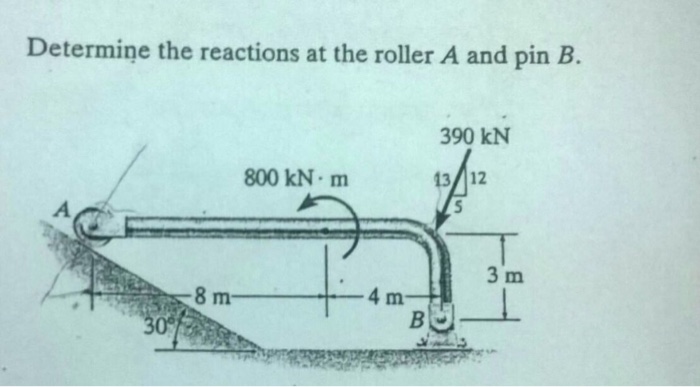
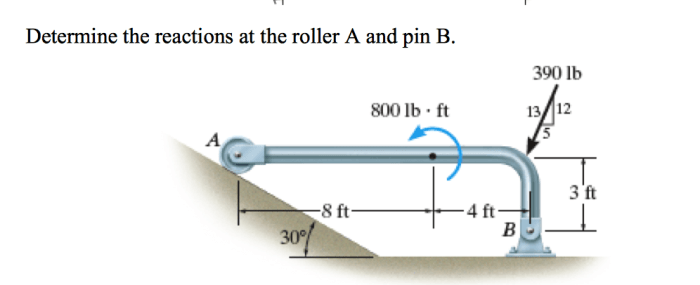
Embark on a journey to determine the reactions at the roller A and pin B, two critical components in engineering structures. These supports play a pivotal role in transferring loads and maintaining stability, and understanding their behavior is essential for structural analysis and design.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the concepts of roller and pin supports, exploring their reactions, assumptions, and limitations. We will uncover the methods used to determine reactions at these supports, delving into the equilibrium equations that govern their behavior.
Through practical examples, we will illustrate the calculation process, empowering you with the knowledge to analyze and design structures with confidence.
Roller Support Reactions: Determine The Reactions At The Roller A And Pin B
Roller supports allow for movement in one direction while preventing movement in the perpendicular direction. They consist of a cylindrical roller that rests on a flat surface. The reaction forces at a roller support are:
- Vertical reaction: Equal to the applied load in the vertical direction.
- Horizontal reaction: Zero, as the roller can only resist vertical movement.
Assumptions and Limitations:* The roller is assumed to be frictionless.
- The surface is assumed to be smooth and flat.
- The load is applied perpendicular to the surface.
Pin Support Reactions
Pin supports allow for rotation about a fixed point while preventing translation in any direction. They consist of a pin that is inserted into a hole in the supported member. The reaction forces at a pin support are:
- Vertical reaction: Equal to the vertical component of the applied load.
- Horizontal reaction: Equal to the horizontal component of the applied load.
- Moment reaction: Equal to the moment about the pin caused by the applied load.
Assumptions and Limitations:* The pin is assumed to be frictionless.
- The hole is assumed to be smooth and cylindrical.
- The load is applied at the pin location.
Determining Reactions at Roller and Pin Supports
The reactions at roller and pin supports can be determined using equilibrium equations. For a roller support, the sum of the vertical forces must be zero:$$\sumF_y=0$$For a pin support, the sum of the forces in both the x and y directions must be zero, and the sum of the moments about the pin must be zero:$$\sumF_x=0$$$$\sumF_y=0$$$$\sumM=0$$These equations can be used to solve for the unknown reaction forces.
Applications of Roller and Pin Supports
Roller and pin supports are used in a variety of engineering structures, including:
- Bridges
- Buildings
- Machines
- Vehicles
Advantages of Roller Supports:* Allow for thermal expansion and contraction.
- Reduce friction and wear.
- Easy to install and maintain.
Disadvantages of Roller Supports:* Can only resist forces in one direction.
May be noisy or unstable under certain conditions.
Advantages of Pin Supports:* Allow for rotation and prevent translation.
- Can resist forces in multiple directions.
- Provide a stable and secure connection.
Disadvantages of Pin Supports:* Can be more difficult to install and maintain than roller supports.
May introduce stress concentrations around the pin.
FAQ
What are the key differences between roller and pin supports?
Roller supports allow movement in one direction, while pin supports fix the supported member in both translational directions but allow rotation.
How are reactions at roller and pin supports determined?
Reactions are determined using equilibrium equations, which consider the forces and moments acting on the supported member.
What are the applications of roller and pin supports in engineering?
Roller and pin supports are widely used in bridges, buildings, machines, and vehicles to transfer loads and maintain structural stability.