What is the sharpe ratio of the best feasible cal – The Sharpe ratio is a risk-adjusted performance measure that evaluates the excess return of an investment relative to its standard deviation. It is widely used in financial analysis to assess the risk-reward profile of different investments. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the Sharpe ratio, including its calculation, interpretation, comparison, limitations, and applications.
1. Sharpe Ratio Definition
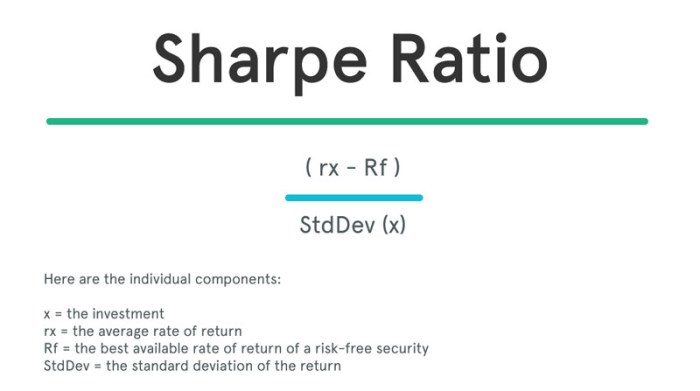
The Sharpe ratio is a risk-adjusted performance measure that evaluates the excess return of an investment relative to its standard deviation. It provides insights into the relationship between risk and reward, allowing investors to compare different investments based on their risk-adjusted returns.
2. Calculation of Sharpe Ratio: What Is The Sharpe Ratio Of The Best Feasible Cal

The Sharpe ratio is calculated using the following formula:
Sharpe Ratio = (Rp – Rf) / σp
- Rp is the expected return of the portfolio or investment.
- Rf is the risk-free rate, which is the return on a safe investment, such as a government bond.
- σp is the standard deviation of the portfolio or investment, which measures the volatility of returns.
3. Interpretation of Sharpe Ratio
A higher Sharpe ratio indicates that an investment has a higher excess return relative to its risk. Positive values indicate that the investment has outperformed the risk-free rate, while negative values indicate underperformance.
Generally, a Sharpe ratio of:
- Less than 1: The investment is considered to be relatively risky and may not be suitable for all investors.
- Between 1 and 2: The investment is considered to have a moderate level of risk and may be suitable for investors with a higher risk tolerance.
- Greater than 2: The investment is considered to have a low level of risk and may be suitable for investors with a lower risk tolerance.
4. Comparison of Sharpe Ratios

Sharpe ratios can be used to compare different investments based on their risk-adjusted returns. The higher the Sharpe ratio, the more attractive the investment is relative to its risk. Investors can use the Sharpe ratio to identify investments that offer a balance between risk and return.
For example, an investment with a Sharpe ratio of 1.5 may be considered more attractive than an investment with a Sharpe ratio of 0.8, as it offers a higher excess return relative to its risk.
5. Limitations of Sharpe Ratio
While the Sharpe ratio is a useful risk-adjusted performance measure, it has certain limitations:
- It assumes that returns are normally distributed, which may not always be the case.
- It does not consider other risk factors, such as liquidity risk or currency risk.
- It is backward-looking and may not be reliable for predicting future performance.
6. Applications of Sharpe Ratio
The Sharpe ratio is widely used in practice for:
- Portfolio management: To optimize portfolios and select investments that offer a favorable balance between risk and return.
- Performance evaluation: To assess the performance of investment managers and compare it to benchmarks.
- Risk assessment: To identify investments with appropriate risk levels for different investor profiles.
FAQ Section
What is the formula for calculating the Sharpe ratio?
Sharpe ratio = (Expected return – Risk-free rate) / Standard deviation of return
How do I interpret the Sharpe ratio?
A higher Sharpe ratio indicates a higher risk-adjusted return. Generally, a Sharpe ratio above 1 is considered good, while a Sharpe ratio below 0 indicates that the investment is underperforming the risk-free rate.
How can I use the Sharpe ratio to compare different investments?
The Sharpe ratio allows you to compare the risk-adjusted performance of different investments. A higher Sharpe ratio indicates that the investment has a better risk-reward profile.